Mass Bitcoin Miner Departure May Drive BTC Under $60,000
However, historical patterns show Bitcoin typically recovers to its energy-based valuation following extended bear markets, with current models suggesting a fair value around $121,000.

A crucial Bitcoin (BTC) indicator that monitors the cost of electricity required to mine one coin is sending concerning signals to bullish investors, with what's being described as a "miner exodus" contributing to the pessimistic market outlook.
Key takeaways:
- BTC could fall toward the $59,000–$74,000 miner cost zone.
- Big hash rate drops often precede rebounds toward Bitcoin's energy value at $121,000.
Mining data hints BTC may decline below $60,000
According to data from Capriole Investments, a crypto-focused hedge fund, the average electricity costs required to mine a single Bitcoin are estimated at $59,450 as of January, while the total net production expenditure stands at approximately $74,300.
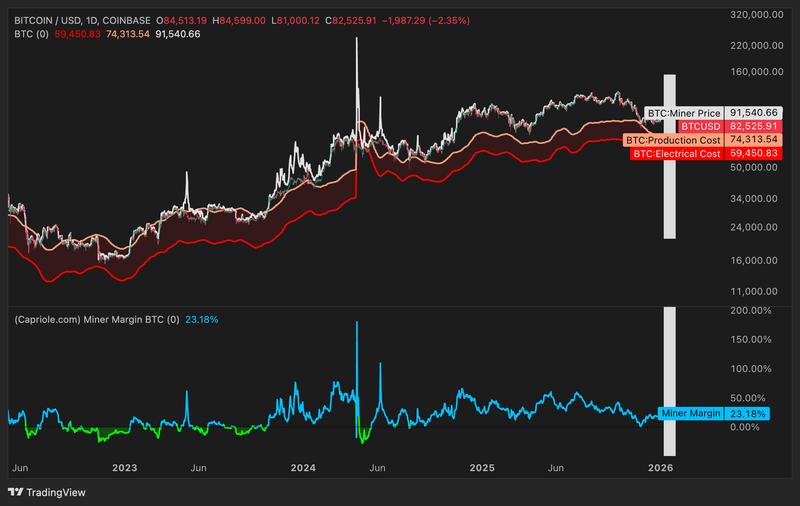
On Friday, Bitcoin was changing hands at approximately $82,500, maintaining levels above the estimated operational costs for miners.
According to Charles Edwards, the founder of Capriole Investments, numerous miners have the capability to sustain operations even if prices drop below their average production costs. The market has potential to descend toward the $74,300–$59,450 range before mining operations experience significant financial pressure, he noted.
"This has expanded the potential range for near-term downside," he said, further citing an ongoing "Bitcoin miner exodus" behind the bearish outlook.
The Bitcoin hash rate experienced a decline to levels last observed in mid-2025 by the end of January, with some market observers theorizing that BTC miners redirected their computational resources toward powering artificial intelligence operations instead. Meanwhile, other analysts attributed the hash rate decline to severe winter weather conditions affecting the United States.
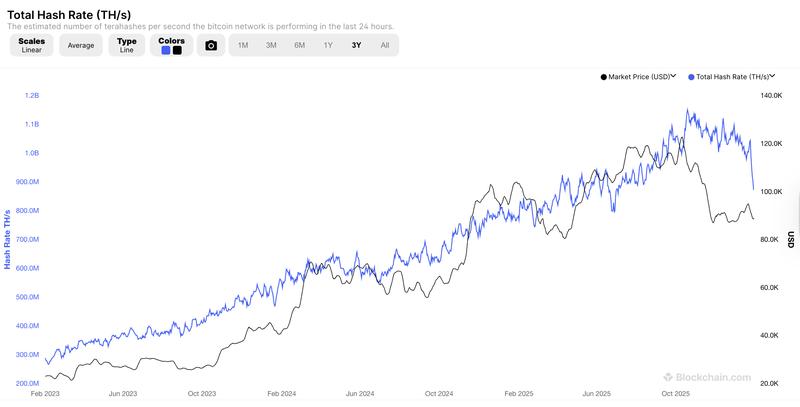
Hash rate dips could be bullish for Bitcoin
According to Jeff Feng, co-founder of Sei Labs, Bitcoin has experienced hash rate declines in the past and subsequently recovered.
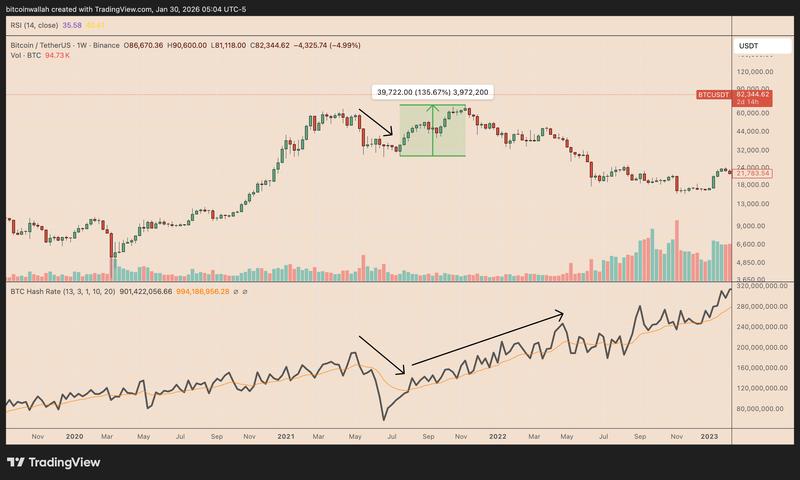
When certain mining operations cease, the network automatically adjusts mining difficulty downward over a period of time. This adjustment makes the mining process easier and more cost-effective for miners who continue operating, thereby ensuring network stability.
Following China's mining ban in 2021, as an example, the hash rate plummeted approximately 50%, and BTC prices dropped from roughly $64,000 down to $29,000. However, the cryptocurrency's price rebounded to $69,000 in just five months.
Based on its energy value—a metric that calculates Bitcoin's fair value using the network's energy consumption and production inputs—Bitcoin's fair price stood at approximately $120,950 as of Friday.
Historical data demonstrates that BTC tends to recover toward its energy-based valuation following extended periods of price decline.
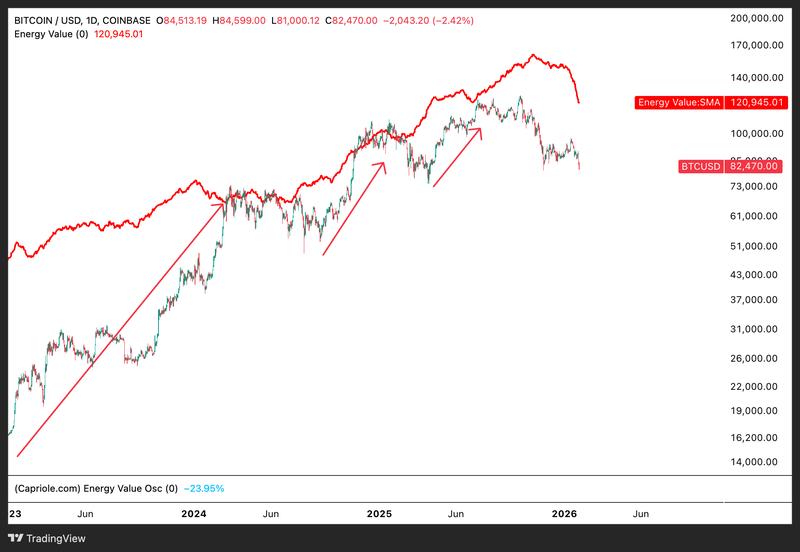
In Bitcoin's case, this pattern indicates that the price may establish a bottom somewhere within the range of $74,300 to $59,450, with any subsequent recovery potentially initiating a mean-reversion movement back toward the energy value price.
