North Korean Crypto Malware Operations Exposed by Google Cloud Security Team
Google Cloud's Mandiant division has been monitoring suspected North Korean cybercriminals since 2018, with artificial intelligence enabling an unprecedented expansion of their malicious activities starting in November 2025.

Cybercriminals with suspected ties to North Korea are intensifying social engineering operations that specifically focus on cryptocurrency platforms and financial technology enterprises, introducing sophisticated malware variants created to extract confidential information and pilfer digital currency holdings.
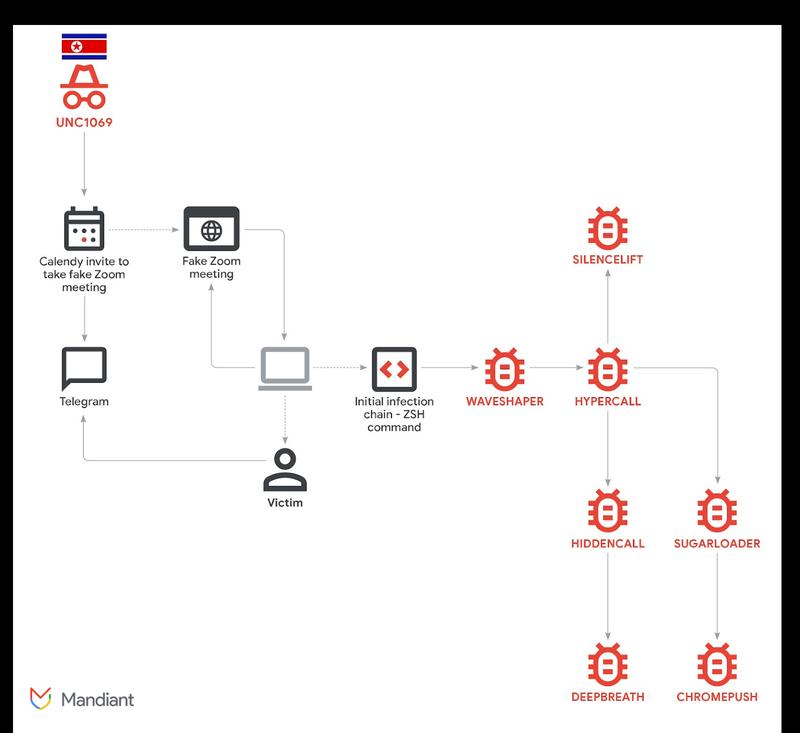
According to a Tuesday disclosure from Mandiant, a cybersecurity company based in the United States that functions as part of Google Cloud, a threat group identified as UNC1069 has introduced seven distinct malware variants in a recent operation, all engineered to collect and transmit victim information.
The offensive operation leveraged social engineering tactics that incorporated hijacked Telegram user accounts and fraudulent Zoom conference calls featuring deepfake video content created using artificial intelligence technologies.
"This investigation revealed a tailored intrusion resulting in the deployment of seven unique malware families, including a new set of tooling designed to capture host and victim data: SILENCELIFT, DEEPBREATH and CHROMEPUSH," the report states.
According to Mandiant's assessment, this activity signals a broadening of the collective's operational scope, with primary focus directed toward cryptocurrency businesses, software development professionals and venture capital investment firms.
Among the malicious software deployed were two recently identified, advanced data-extraction viruses, designated CHROMEPUSH and DEEPBREATH, which are engineered to circumvent critical operating system security features and obtain unauthorized access to sensitive personal information.
Mandiant has maintained surveillance of the threat actor with "suspected" connections to North Korea since 2018, however artificial intelligence technological progress enabled the malicious operator to amplify their operations and incorporate "AI-enabled lures in active operations" for the first time in November 2025, as documented in a contemporaneous report from the Google Threat Intelligence Group.
Cointelegraph contacted Mandiant for additional details regarding the attribution, but had not received a response by publication.
Attackers are stealing crypto founder accounts to launch ClickFix attacks
In a specific intrusion scenario detailed by Mandiant, the attackers leveraged a hijacked Telegram account that belonged to a cryptocurrency company founder to establish initial communication. The targeted individual received an invitation to participate in a Zoom video conference that displayed a manipulated video stream in which the threat actor pretended to be experiencing technical audio difficulties.
The attacker then directed the user to run troubleshooting commands in their system to fix the purported audio issue in a scam known as a ClickFix attack.
The provided troubleshooting commands had embedded a hidden single command that initiated the infection chain, according to Mandiant.
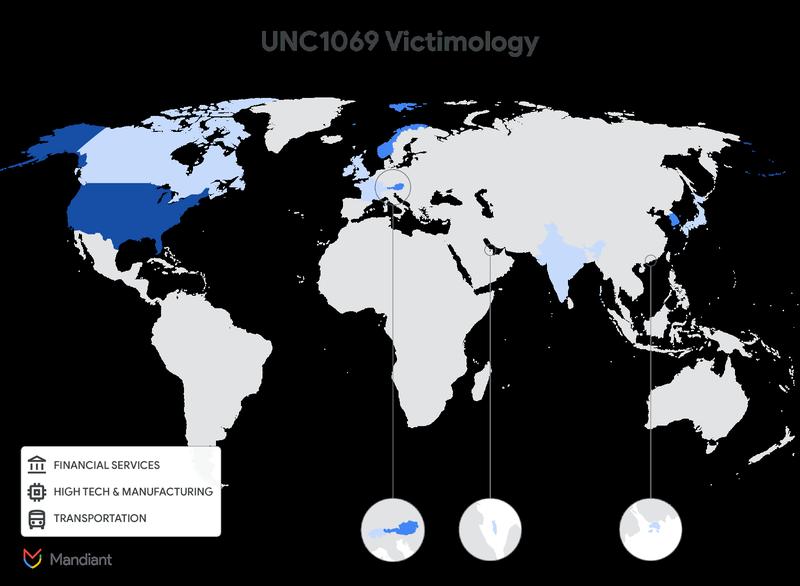
Illicit operators with connections to North Korea have maintained an ongoing threat profile targeting both cryptocurrency investors and organizations native to the Web3 ecosystem.
In June 2025, four North Korean operatives infiltrated multiple crypto firms as freelance developers, stealing a cumulative $900,000 from these startups, Cointelegraph reported.
Earlier that year, the Lazarus Group was linked to the $1.4 billion hack of Bybit, one of the largest crypto thefts on record.