Ethereum's Journey to Quantum Security Hits 20% Completion Mark: Exclusive Interview
Researcher Antonio Sanso details Ethereum's comprehensive roadmap for achieving post-quantum protection, which includes sweeping modifications to execution layers, consensus mechanisms, and data blob architecture.

According to Antonio Sanso, a cryptography specialist working with the Ethereum Foundation, the blockchain network will achieve quantum resistance well in advance of any potential quantum-based threats materializing.
"The Ethereum Foundation (EF), together with the broader Ethereum community, is dedicating massive resources to addressing this challenge," he shared in conversation with Cointelegraph.
"The theoretical research component has likely already been resolved. We're now transitioning into the implementation phase of these solutions. We maintain strong confidence that we'll successfully achieve our targets within the established timeframe."
Post-quantum (PQ) security has been designated as a critical strategic objective by the EF. The organization revealed on Jan. 24 the establishment of a dedicated Post Quantum team under the leadership of Thomas Coratger. Beginning Feb. 4, Sanso will spearhead newly created biweekly All Core Devs discussions focused specifically on post-quantum protection measures.
The scope of this initiative is extensive. According to Sanso's explanation, comprehensive upgrades are required across Ethereum's execution layer, consensus mechanisms, and data availability infrastructure.
"Implementing a post-quantum framework isn't limited to a single component — we're looking at multiple major sections of Ethereum that require migration," he explained.
"What's encouraging is our substantial groundwork spanning many months, potentially years. We've developed a concrete strategy, and implementation should unfold over the coming years."
One-fifth of the way to the finish line
When questioned about quantifying the current development progress, Sanso indicated that advancement varies across different layers, "so there isn't a single percentage applicable to all three components. However, as a rough estimate, we're approximately 20% complete."
The newly initiated biweekly discussions will examine various approaches' advantages and compromises. Post-quantum development networks featuring multiple clients are currently operational, with a comprehensive PQ roadmap slated for imminent release. This roadmap aims for what EF researcher Justin Drake characterizes as "a full transition in coming years with zero loss of funds and zero downtime."
Achieving quantum resilience for Ethereum represents merely one component of a comprehensive blockchain transformation under the Lean Ethereum initiative. This ambitious plan seeks to enhance Ethereum's speed, reduce complexity, and strengthen decentralization through zero-knowledge (ZK) technology implementation, simultaneously fortifying defenses against quantum computing threats.
Comparison to Bitcoin
Ethereum's proactive approach to quantum protection stands in marked contrast to Bitcoin's position, where prominent figures including Adam Back and Michael Saylor have minimized urgency for modifications, citing projections that functional quantum computers remain years or potentially decades distant.

These projections hold validity, though with important qualifications. During DevConnect in Buenos Aires, co-founder Vitalik Buterin highlighted that while median forecasts place cryptography-breaking quantum computers around 2040, a 20% probability exists for such technology emerging by 2030.
Interestingly, a smaller portion of Bitcoin (BTC) faces actual quantum vulnerability, with approximately 6 million BTC — primarily held in legacy addresses with exposed public keys — currently susceptible to quantum attacks.
"From a purely technical standpoint, migration is less complex," Sanso clarified. "However, they'll likely encounter challenges at the social coordination level... achieving consensus on implementation approaches."
"Ethereum doesn't face this particular obstacle, but... from a technological perspective, we have considerably more infrastructure requiring migration," he noted. "While we share the common requirement of modifying execution transaction signatures, among our challenges — spanning execution layer, consensus, and data availability — the execution layer presents the simplest case. The remaining two present greater complexity."
What happens if quantum computers arrive early?
Sanso's personal projection for quantum computer capability breakthrough centers on the mid-2030s timeframe. His expectation places Lean Ethereum completion somewhere within the 2028 to 2032 window.
Considering the unexpected rapid emergence of large language models and ZK-proofs (which arrived substantially ahead of predictions), quantum computers capable of compromising blockchains might become reality before protective measures reach full implementation.
Enhanced protection for your Ether (ETH) holdings can be implemented immediately by transferring assets to fresh, previously unused addresses, thereby keeping public keys unexposed (quantum computers utilize reverse engineering to extract private keys from public ones through Shor's algorithm).
Looking ahead, intelligent wallet systems leveraging account abstraction combined with post-quantum signature schemes will safeguard your ETH.
"Our approach involves implementing a new post-quantum algorithm, most likely based on lattice or hash functions. Integration will occur through account abstraction mechanisms."
PQ signatures are much larger
During November's DevConnect conference, Zknox showcased a hardware wallet featuring post-quantum Dilithium signature technology that maintains compatibility with Ethereum's current infrastructure.
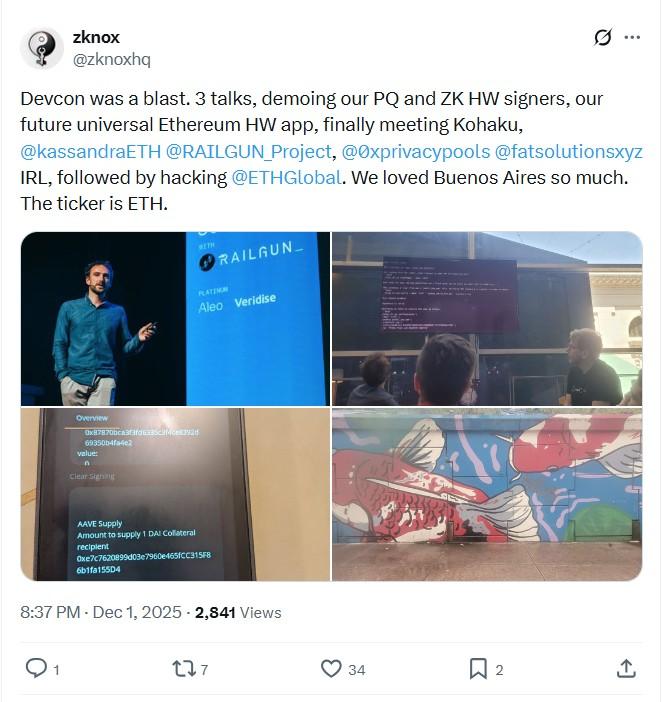
Post-quantum signatures, however, are substantially larger, with the most compact option, Falcon, still measuring 10 times the size of current Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) signatures.
According to Sanso's explanation, implementing the lattice-based solution using Solidity results in prohibitively expensive gas costs. An Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP) exists for creating a precompile that would process this functionality external to the core protocol, thereby improving efficiency and lowering expenses.
The broader challenge of integrating signatures 10 times larger than existing ones into the blockchain will necessitate multiple complementary strategies, including leveraging ZK-STARKs for signature compression.
Emergency quantum upgrade
Additionally, Buterin formulated a contingency strategy in March 2024 addressing potential quantum attacks, incorporating a hard fork alongside a verification method enabling ETH holders to authenticate legitimate ownership of specific addresses before transitioning to PQ addresses with equivalent balances.
This contingency plan has advanced considerably, according to Sanso, with development underway on a system allowing ETH holders to employ ZK-proofs for securely demonstrating possession of correct address seeds.
"This has been an active development focus for us. With any luck, we'll have a project demonstration prepared for either EthCC Cannes or Devcon in India."
Depending on approved EIPs, this verification system could potentially integrate into the planned migration to PQ signatures. Users could authenticate address ownership, subsequently deactivating the quantum-vulnerable ECDSA component of their accounts.
"This EIP enables self-activation, allowing users to declare they're terminating the elliptic curve functionality on their EOAs. You maintain your existing address, with the sole method for transferring assets being a combination of account abstraction and seed proof verification."
"This will likely receive attention in upcoming forks, and personally, I believe it represents the correct direction."
Sanso emphasized that selecting which EIPs to incorporate involves an extended deliberation process with ultimate determination resting with the community.
The inaugural All Core Devs PQ "breakout room" discussion is scheduled for Feb. 4, 2026, he confirmed.
Per Drake's statement, the biweekly meetings will "focus on user-facing security, covering dedicated precompiles, account abstraction and longer-term transaction signature aggregation with leanVM."